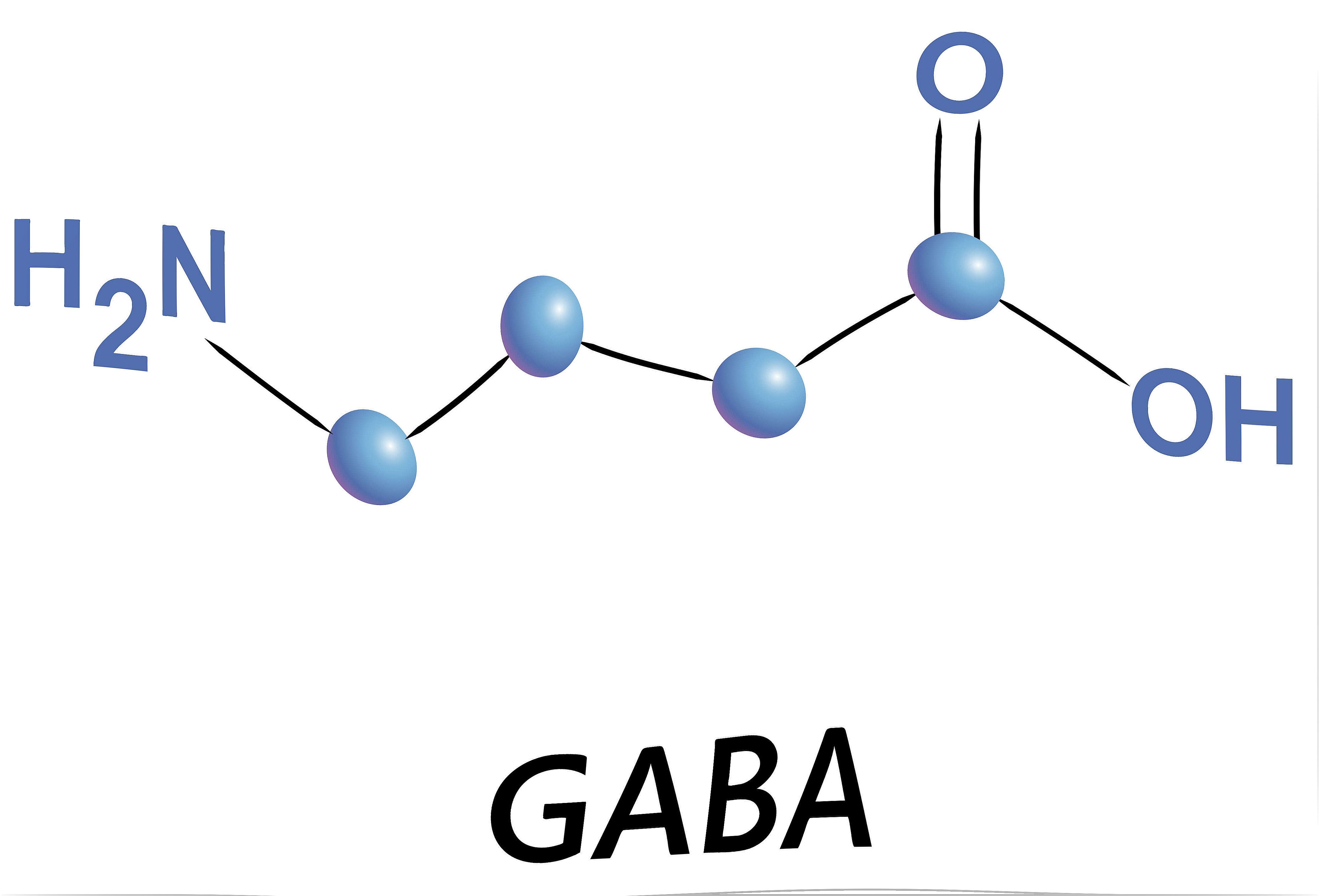
Gamma-aminobutyric Acid (GABA)
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is one of the most important inhibitory neurotransmitters in the body. Neurotransmitters are substances used by the nervous system in synapse or nerve impulse transmission processes. These functions are carried out by the main nerve cells, the neurons.
As a general rule, it is obtained from the glutamate that we obtain in the diet or through its synthesis. It usually occurs in the cerebellum (GABAergic neurons), in the basal ganglia, and in certain parts of the spinal cord. It can also be obtained through certain sedative plants, such as valerian.
Glutamate usually functions as an “exciter” in the body, accelerating neuronal activity. This neurotransmitter is present in stressful and alert situations, but it is also involved in normal functions, such as coordination or memory. The person will feel irritable, restless, his heart will beat faster and may even have insomnia.
Functions of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
GABA directly affects the central nervous system (CNS), reducing brain activity. This substance allows you to balance brain activation so that optimal levels of arousal are maintained at all times. Therefore, it intervenes in the development of sleep, relaxation, pain perception and other endocrine functions.
It is the mechanism that the body has to combat the effects of stress, insomnia, neuralgia, etc. At other times, it absorbs excess adrenaline and certain toxins, inducing a state of relaxation and well-being.
There are other lesser known functions, but just as important:
- Supports the immune system.
- It releases somatotropin (the growth hormone that is involved in muscle development and the prevention of certain diseases).
GABA Pharmacology
There are drugs that act as CNS depressants in a way that favors the production of GABA. The best known are the benzodiazepines (diazepam).
When there are alterations in the normal levels of GABA we find psychiatric and neurological diseases. However, the intake of alcohol, drugs, smoking and other medications, such as Valium, can also change GABA levels.
Associated pathologies
Alcohol enhances or promotes the inhibition of neuronal activity by GABA, which produces some euphoria. Too much GABA can lead to respiratory failure and even death. Some of the most frequent diseases due to these alterations are:
- Epilepsy.
- Anxiety.
- Depression.
- Schizophrenia.
Their treatment includes the aforementioned medications as well as other drugs or practices recommended by the medical team. In anxiety, GABA levels are decreased, which is why the CNS is overexcited. In addition, it is usually associated with stress.
Likewise, epilepsy may be due to this factor, apart from the genetic component it has. The hallucinations (olfactory and gustatory) typical of schizophrenia are also associated with a decrease in the levels of this neurotransmitter.
High GABA levels, as we have seen, are associated with relaxation that, if not controlled, can lead to depression and even apathy in the subject. Several studies claim that these abnormal values may be related to Alzheimer’s.
Regarding sleep disorders we can mention insomnia and sleep paralysis. In the first case, the low levels of the compound do not allow the characteristic relaxation of the process. In the second, the high GABA values make the person wake up while their body is in REM phase and immobilized.
Sometimes it is also administered in patients with chronic pain, since it has the ability to inhibit the sensation of pain. At the sports level, these compounds are used by athletes to calm discomfort and promote tissue growth. However, it must be controlled by professionals to avoid addiction or other effects on a physiological or anatomical level.
Important facts about GABA
GABA analog drugs have side effects. One of the serious consequences of its use is the possible risk of dependence due to its addictive potential. Therefore, it should not be taken if it is not under a medical prescription.
In case your doctor has indicated this type of medication, follow their indications and, if you have doubts, comment them before making any type of modification on your own.