Coccidioidomycosis Or San Joaquin Fever
Coccidioidomycosis generally affects the lungs. However, the disease can spread and attack the bones and central nervous system mainly
Coccidioidomycosis is a systemic infection caused by fungi called Coccidioides. These belong to the dimorphic species. This disease is also called valley fever or San Joaquin fever.
It is called San Joaquin or Valley fever because Coccidoides immitis fungi are found exclusively in the San Joaquin Valley. This is an area that is located in southern California, USA.
For its part, the variety Coccidioides posadasii , which also gives rise to coccidioidomycosis, is present in the arid and semi-arid soils of Central and South America. During the dry stage, the mushrooms grow and are revitalized. During the rainy season, the spores spread.
General aspects of coccidioidomycosis
The main characteristic of coccidioidomycosysis is that it generates small nodules in the lung. These spread and attack the bones, the central nervous system, or the skin. In fact, they can attack any organ in the human body.
The fungi that cause the disease are generally underground. They are 20 or 25 centimeters from the surface. It is very common for them to be present in caves and similar sites.
However, when there are strong winds or tillage work, the spores spread through the air.
Risk factors for getting the infection are :
- Work in an activity that exposes the dust on the floor.
- Belonging to the African American or Asian ethnic group.
- Have a weakened immune system.
- Being in the third trimester of pregnancy.
- Live in an endemic area.
- Be over 60 years of age.
In Arizona and northern Mexico there is an increased risk of infection between June and July, and October and November. In California, the risk is present from June to November equally.
Clinical forms

Coccidioidomycosis is usually acquired by inhalation of the spores. Therefore, the lungs are almost always the initial focus of infection. In this case, the most frequent symptoms are:
- Cough
- Fever and chills
- Headaches and muscle aches
- Stiff neck or shoulders
- Night sweats
Sometimes skin symptoms appear after a few months after contracting coccidioidomycosis. These include papules, ulcers, warty plaques, and nodules.
These injuries can be single or multiple. There are also cases in which the disease spreads to the bones and causes discomfort in them.
If coccidioidomycosis affects the central nervous system, it causes meningitis or inflammation of the meninges. This is the most serious form of the disease. If it is not treated properly and on time, in 90% of cases it causes the death of the patient.
Diagnosis of the disease
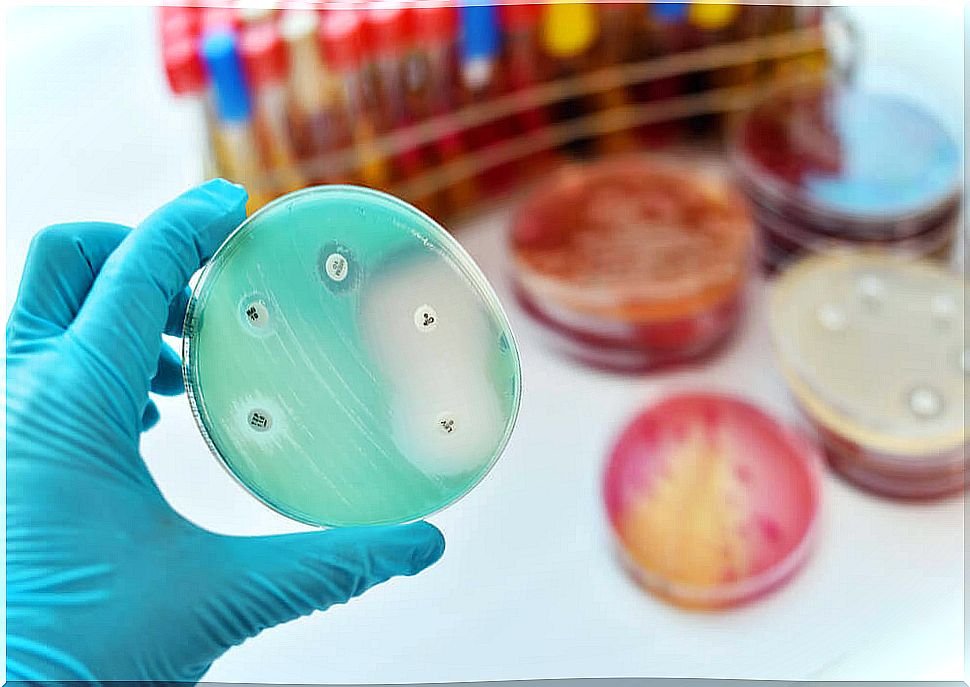
Coccidioidomycosis is diagnosed from clinical, laboratory, and imaging tests.
Although no definite patterns have been established, testing is the main guiding element. They are only practiced if the patient lives or has traveled to one of the endemic areas.
Thus, the main tests are:
- Taking samples of infected tissues. They can be sputum or cerebrospinal fluid. When examined under a microscope, they reveal the presence of fungi or fungal spherules, products of this.
- Serological tests. They reveal the presence of antibodies generated against the fungus. More than a third of those with coccidioidomycosis are serologic test negative.
- Skin test. It is not very reliable as anyone ever exposed to the fungus tests positive for life, even if they are not infected.
- Chest X-rays. They reveal the lung cavities caused by coccidioidomycosis. They are relatively reliable tests.
People undergoing treatment usually heal. However, the fungi usually persist for several years, which implies quite extensive treatments over time.
In severe cases of pulmonary coccidioidomycosis, surgery will be necessary to repair the lung cavities.
In many cases, surgical drainage of abscesses in bones and joints are also necessary.
Also, when the disease attacks the central nervous system and causes meningitis, the outcome is often unpredictable.