Corneal Tumors: Pinguecula And Pterygium
Eye disorders are more common than they appear and in many cases can go unnoticed. Routine eye exams from time to time can facilitate the early diagnosis of abnormalities such as pinguecula or pterygium.
The eyes are the fundamental organ of one of the most important senses: sight. Therefore, it is advisable to pay attention to any anomaly. In this sense, there are two fairly frequent corneal tumors or eye conditions; the pinguecula and the pterygium, and we will talk about this this time.
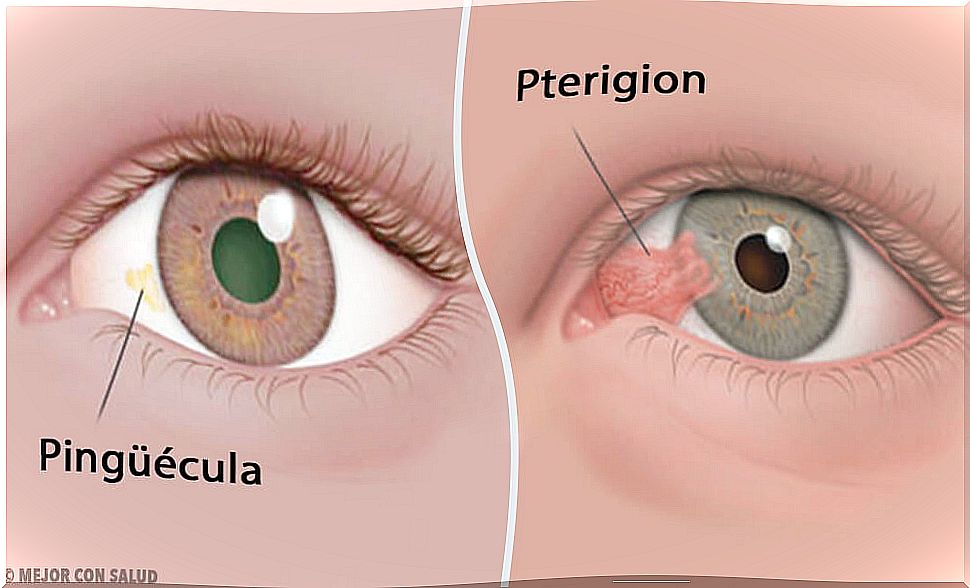
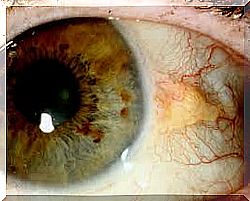
Both conditions are the result of degeneration of the conjunctiva. The pinguecula appears as a small lentil or button in the white area of the eye (sclera), sometimes imperceptible. For their part, pterygiums are the result of an abnormal growth of the conjunctiva, due to an inflammatory process.
Although the size of the pinguecula is usually insignificant, it can increase over time. In most cases its volume does not directly affect vision. In fact, some people may file more than one without being aware of it.
Read on to learn about the most common causes of pinguecula, its symptoms, treatments, and its differences from pterygium.
Corneal tumors
Conjunctival and corneal tumors comprise a wide and varied spectrum of conditions. These tumors are grouped into two broad categories of congenital and acquired lesions.
Acquired lesions are subdivided, in turn, according to the origin of the mass, into superficial epithelial tumors, melanocytes, vascular, fibrous, neural, histiocytic, myxoid, myogenic, lipomatous, lymphatic, leukemic, metastatic and secondary.
What are the causes of pinguecula?
According to the specialists of the American Academy of Ophthalmology, among the causes of pinguecula are :
- Exposure to dust and wind.
- Overexposure to ultraviolet light.
- Body fat.
- Dry eye syndrome
- Hormonal changes.
- Consumption of some medications.
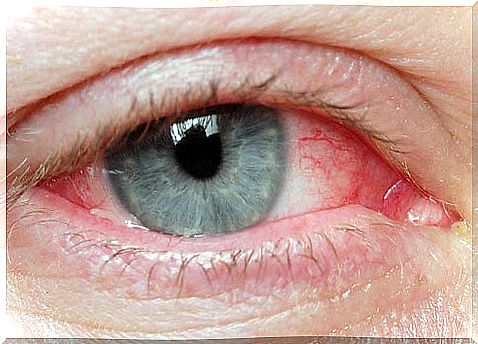
Pinguecula symptoms
- Itching in the eye or redness of the eyeball, especially near the cornea, pupil and iris.
- Eye dryness
- Irritation of the affected area.
- Constant swelling
- Foreign body sensation.
How is pinguecula treated?
This condition usually does not require treatment. If it results in bothersome symptoms, your ophthalmologist may recommend the use of lubricating drops.
However, in severe cases in which this injury directly affects the sight or gives rise to symptoms that do not disappear with the use of lubricating drops, surgical treatment can be used.
Among these cases, a very severe inflammation of the conjunctiva of the eye stands out, which leads to redness and constant itching.
It should be noted that the surgery used is ambulatory, with local anesthesia, and does not take too long. However, all surgical intervention carries certain risks, so it will always be the last option.
After the intervention, the patient must wear a maximum protection patch for two days, unless the specialist recommends otherwise.
Differences between pinguecula and pterygium
Despite the fact that both conditions are the consequence of anomalous processes of the conjunctiva, we are talking about two different conditions.
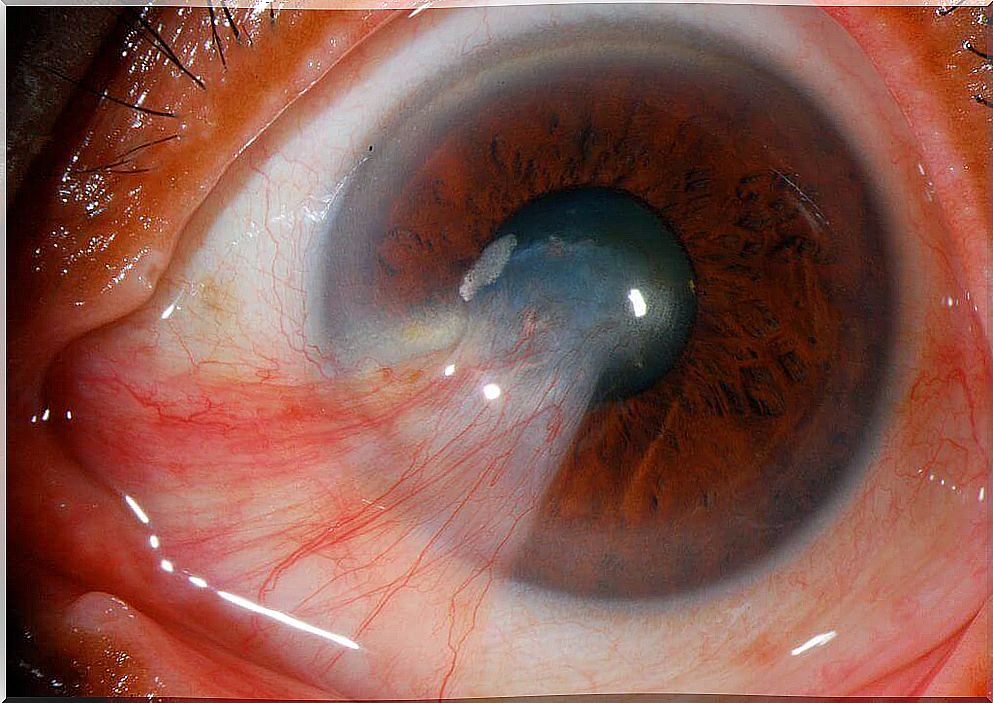
The pterygium consists of an ocular anomaly that manifests itself through the formation of a fleshyness in the eyes, of a color similar to that of the skin, different from the yellowish color of the pinguecula.
Nor are they located in the same place. The pterygium usually develops from one end of the conjunctiva towards the cornea, while the pinguecula usually appears directly on the sclera, and rarely affects the cornea.
Also, if the pterygons grow to a considerable size, they can alter the surface of the eye and lead to visual problems.
Similarities between pinguecula and pterygium
The first similarity, as we have been commenting throughout the article, is that both conditions are the consequence of an anomaly of the conjunctiva, the thin layer of connective tissue that covers the eyeball.
Both conditions, in their early stages, give rise to similar symptoms, so it is not uncommon for them to be confused.
Faced with these conditions, specialists recommend taking preventive measures. It is important to avoid its most direct cause, exposure to ultraviolet rays. This is achieved not by using any type of sunglasses, but those that present a filter against UV rays.
Another important factor that triggers both conditions is age. In fact, they are much more common in people over 40 years of age. Routine eye exams will allow early detection of this and other more serious eye problems.