Tachypnea: Rapid And Shallow Breathing
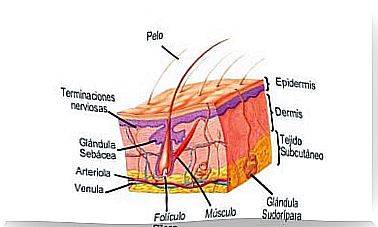
The basal respiratory rate is one of the vital signs that should be monitored in a medical consultation. The rate of breaths within normal range depends on age and individual condition, but ranges from 12 to 20 per minute. Tachypnea is a respiratory rate above this range, corresponding to a value greater than 20 breaths per minute.
Transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN) is the most common and investigated variant of this condition, since it occurs in approximately 1% of newborns, especially if they are premature or are born by cesarean section. If you want to know everything about this topic, keep reading.
What is tachypnea and how is it characterized?
As indicated by the National Library of Medicine of the United States, a normal respiratory rate in an adult ranges between 8 and 16 breaths per minute. In the baby it is much faster, rising to about 44 breaths per minute. This is because their respiratory system has not yet fully matured.
Tachypnea is seen when the respiratory rate is greater than 20 breaths per minute. This term is even more relevant when the patient has rapid and shallow breathing due to lung disease or another cause.
Are hyperventilation and tachypnea the same?
This question does not have an easy answer, as there are discrepancies according to the sources consulted. However, the paradigm can be summed up in the following sentence: tachypnea does not have to translate into deep rapid breathing.
That is, in hyperventilation the air reaches the alveoli, so more carbon dioxide (CO2) is eliminated than the body is capable of producing. This causes hypocapnia, a reduction in the concentration of CO2 in the blood. On the other hand, in tachypnea the respiratory rate increases, but the air does not have to reach the lower respiratory tract.
Symptoms related to tachypnea
The symptoms of tachypnea will depend on the underlying cause. For example, a child with a viral illness will develop a fever, cough, sneeze, and runny nose. However, some of the general clinical signs of the condition are as follows:
- Feeling short of breath This can cause dizziness, confusion, and overwhelm.
- A bluish tinge on the lips and fingertips, under the nails.
- Hold on to the chest when breathing and show retractions. In the latter event, the area below the ribs sags every time you try to inhale.
On the other hand, transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN) presents some related accessory clinical signs, since the baby cannot communicate its condition directly. The newborn may grunt and have abnormally widened nostrils, nodding, retractions, and bluish skin.
When to go to the doctor?
In case of feeling retraction in the chest with each breath and presenting the described areas of bluish color, it is urgent to see a medical professional. If you’ve never had rapid breathing before or your symptoms get worse over time, you should also seek help.
What are the possible causes of tachypnea?
The Kids Health website shows us which are the most common causes of tachypnea, both in neonates and adults. We begin by showing you the etiology of older patients and we dedicate the last section to newborns. Do not miss it.
Asthma
As indicated by the American Academy of Asthma, Allergy and Immunology (AAAAI), asthma is a chronic disease of the lungs that consists of inflammation and hyperactivity of the airways. A patient has the severe variant of this disorder when he needs medium or high doses of inhaled corticosteroids in order to live.
Symptoms of severe asthma can include chronic and recurring cough, wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, tachypnea, and many other metabolic signs. In rare cases, asthma can be fatal to the patient if it is not controlled.

Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
This disease is a chronic condition that causes obstruction of airflow in the lungs, according to the Mayo Clinic. Its symptoms include shortness of breath, wheezing, tachypnea, and mucus production in the respiratory channels.
Exposure to fumes (such as tobacco smoke) and other toxic substances are very conducive to its long-term appearance.
Anxiety and panic
Continued stress over time results in a generalized anxiety pattern that keeps the patient’s body on alert, unconsciously and without a rational basis.
Anxiety, panic, and other negative feelings can cause tachypnea. However, remember that on a medical level it is not exactly the same as hyperventilation.
Other causes of tachypnea in adults
We have collected 3 of the most common causes of tachypnea in adults, but we must name many more, in order to explore the entire etiology of the condition.
Among the rest of underlying diseases that can trigger the disorder we find the following:
- Blood clot in an artery or in the lung: Increased respiratory rate is a typical clinical sign that manifests itself during a pulmonary embolism.
- Heart failure: The heart cannot pump enough oxygen-rich blood to each and every tissue in the body. Therefore, unconsciously, the respiratory rate is increased in order to try to trap more ambient oxygen.
- Small respiratory tract infection: This condition is known as bronchiolitis .
Transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN)
As indicated in the MSD Manuals, TTN occurs in newborns when they try to expel fluids that were housed in their lungs during the gestation period. Being born before term, experiencing a cesarean delivery, being a male and being a twin are risk factors for developing it.
TTN in newborns is not a serious condition. The vast majority of them recover on their own in 2-3 days, when the body gets used to breathing outside the mother’s uterus.
Diagnosis of tachypnea
Tachypnea can be caused by relatively normal situations, such as exercising or going through a time of stress. In case it is a transitory event and does not go away, it is not usually necessary to go to a medical professional. There is not always a disease behind fast, deep breathing.
In any case, if this occurs in a serious way or if it is sustained and worsens over time, the doctor will carry out a series of tests on the patient based on various suspicions. Among all the diagnostic methods we highlight the following:
- Hemogram and blood culture: this is done to rule out a systemic infection, since septicemia and bacteremia can also lead to tachypnea.
- Chest X-ray: to look for or rule out chronic respiratory problems at the lung level.
- Electrocardiogram: as we have said, a heart failure can lead to the appearance of tachypnea.
Treatment of tachypnea
Treatment of a tachypnea will depend entirely on the underlying cause. If rapid, shallow breathing is rooted in an emotional problem, psychological care is always the way to go. If, on the other hand, it is linked to certain medical conditions, it is time to go to pharmacological approaches.
In any case, we must emphasize the following idea: unless it is an emotional pathology, sustained tachypnea is always a medical emergency.
1. Lung infections
If rapid and shallow breathing is the result of an infection in the respiratory tract, it is necessary to prescribe general or specialized drugs, depending on what the pathogen requires. Albuterol and other medications can also be used simultaneously, in order to open the patient’s airways.
2. Chronic lung conditions
Asthma and COPD cannot be cured, but they can be kept at bay. Bronchodilators, inhaled steroids, and combination inhalers can be used to decrease irritation in the bronchial tissue and open the airways.
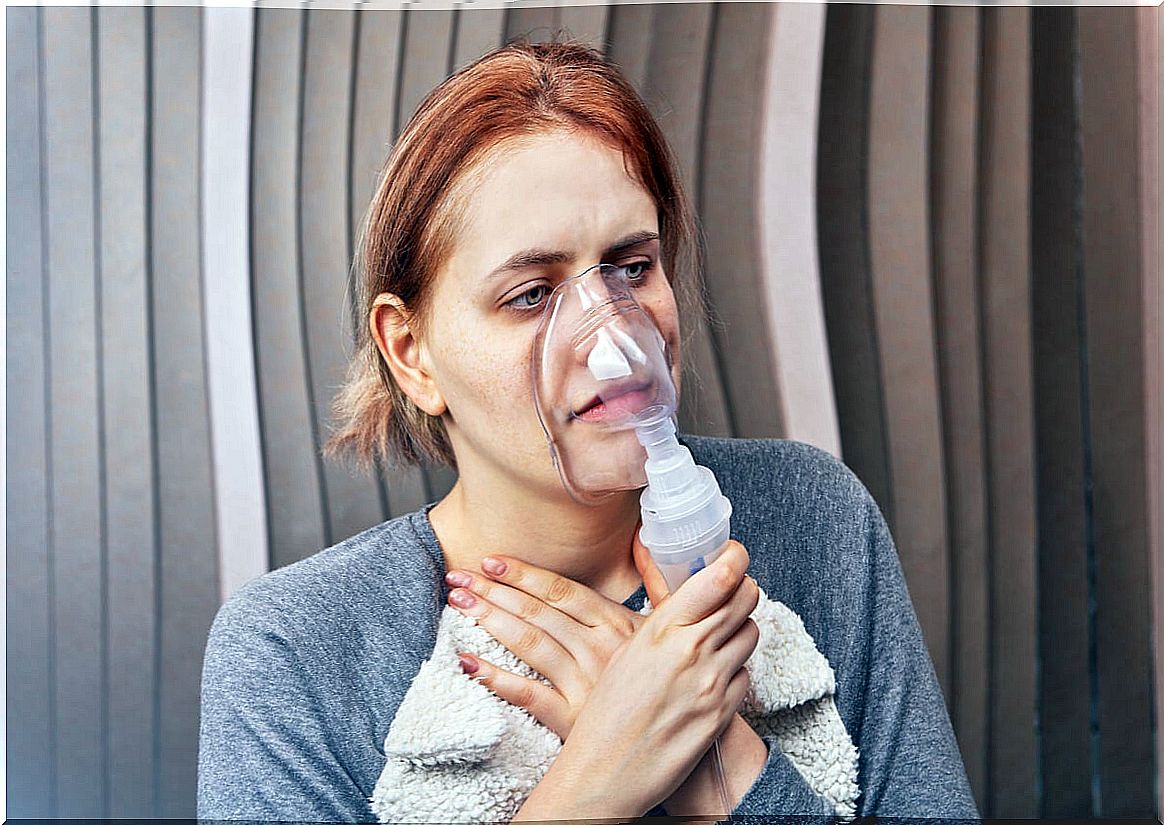
3. Anxiety disorders
If the tachypnea is the product of stress, anxiety, depression or other emotional clinical pictures, the best option is always to go to the psychiatrist and psychologist. In addition to therapy, antidepressant and anxiolytic drugs may be prescribed to manage these symptoms.
Tachypnea should be checked
As you may have seen, the etiology of tachypnea is very extensive and varied. From anxiety to serious heart disorders, rapid, shallow breathing can have many underlying causes.
Although sometimes it has no explanation, if the tachypnea is sustained it is necessary to go to the emergency room quickly.
On the other hand, this increase in respiratory rate can be the result of physical exercise and certain emotional disorders. If you think your breathing is unusual, no matter how slight, visit your doctor.